Many investors turn to Benjamin Graham's so-called “Graham number” to calculate the fair price of a stock. The Graham number is √(22.5 * 5 year average earnings per share * book value per share), which for Dollar General gives us a fair price of $73.51. In comparison, the stock’s market price is $125.79 per share. Dollar General’s current market price is 71.1% above its Graham number, which implies that there is upside potential -- even for a conservative investors who require a significant margin of safety.
The Graham number is often used in isolation, but in fact it is only one part of a check list for choosing defensive stocks that he laid out in Chapter 14 of The Intelligent Investor. The analysis requires us to look at the following fundamentals of Dollar General:
Sales Revenue Should Be No Less Than $500 million
For Dollar General, average sales revenue over the last 5 years has been $56.52 Billion, so in the context of the Graham analysis the stock has impressive sales revenue. Originally the threshold was $100 million, but since the book was published in the 1970s it's necessary to adjust the figure for inflation.
Current Assets Should Be at Least Twice Current Liabilities
We calculate Dollar General's current ratio by dividing its total current assets of $8.1 Billion by its total current liabilities of $6.64 Billion. Current assets refer to company assets that can be transferred into cash within one year, such as accounts receivable, inventory, and liquid financial instruments. Current liabilities, on the other hand, refer to those that will come due within one year. Dollar General’s current assets outweigh its current liabilities by a factor of 1.2 only.
The Company’s Long-term Debt Should Not Exceed its Net Current Assets
This means that its ratio of debt to net current assets should be 1 or less. Since Dollar General’s debt ratio is -0.3, the company has much more liabilities than current assets because its long term debt to net current asset ratio is -0.3. We calculate Dollar General’s debt to net current assets ratio by dividing its total long term of debt of $6.22 Billion by its current assets minus total liabilities of $30.8 Billion.
The Stock Should Have a Positive Level of Retained Earnings Over Several Years
Dollar General had good record of retained earnings with an average of $2.23 Billion. Retained earnings are the sum of the current and previous reporting periods' net asset amounts, minus all dividend payments. It's a similar metric to free cash flow, with the difference that retained earnings are accounted for on an accrual basis.
There Should Be a Record of Uninterrupted Dividend Payments Over the Last 20 Years
Dollar General has offered a regular dividend since at least 2009. The company has returned an average dividend yield of 1.0% over the last five years.
A Minimum Increase of at Least One-third in Earnings per Share (EPS) Over the Past 10 Years
To determine Dollar General's EPS growth over time, we will average out its EPS for 2010, 2011, and 2012, which were $0.37, $0.50, and $0.62 respectively. This gives us an average of $0.50 for the period of 2010 to 2012. Next, we compare this value with the average EPS reported in 2022, 2023, and 2024, which were $10.17, $10.68, and $7.55, for an average of $9.47. Now we see that Dollar General's EPS growth was 1794.0% during this period, which satisfies Ben Graham's requirement.
Based on the above analysis, we can conclude that Dollar General satisfies some of the criteria Benjamin Graham used for identifying for an undervalued stock because it is trading above its fair value and has:
- impressive sales revenue
- just enough current assets to cover current liabilities, as shown by its current ratio of 1.22
- much more liabilities than current assets because its long term debt to net current asset ratio is -0.3
- good record of retained earnings
- an acceptable record of dividends
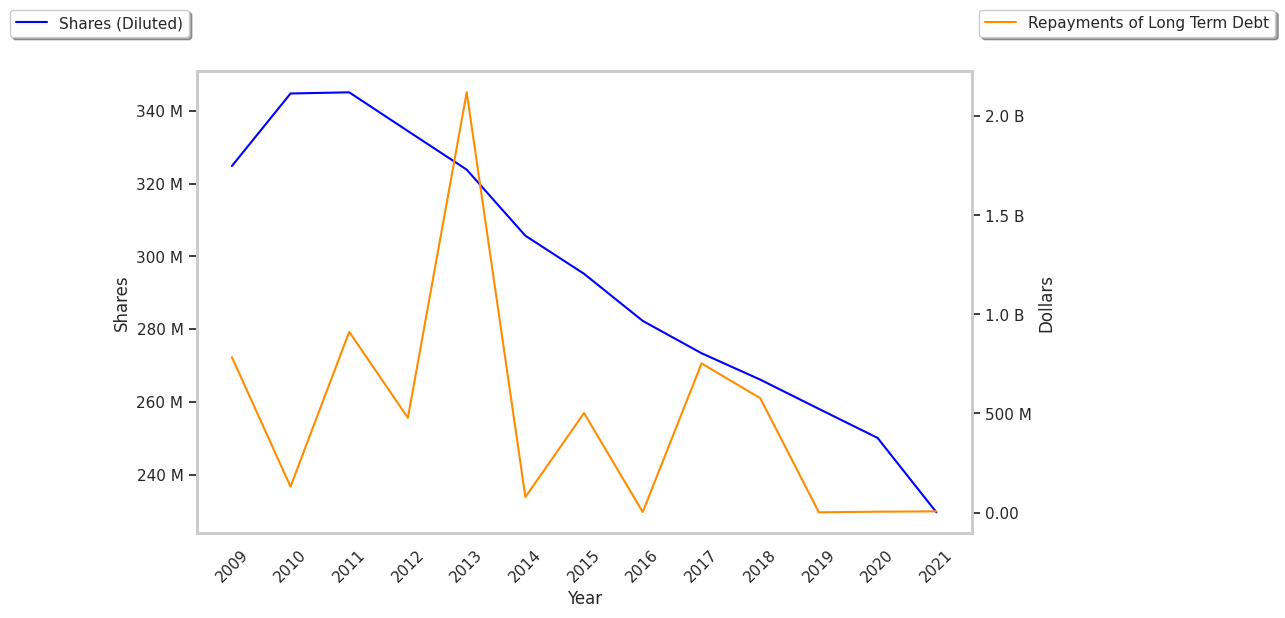
- EPS growth achieved by reducing the number of outstanding shares